LibUI
<a href=“github.com/AndyObtiva/glimmer-dsl-libui”><img alt=“glimmer-dsl-libui” src=“github.com/AndyObtiva/glimmer/blob/master/images/glimmer-logo-hi-res.svg” width=“50” height=“50” align=“right”></a>
LibUI is a Ruby wrapper for libui family.
:rocket: libui-ng - A cross-platform portable GUI library
:wrench: libui-dev - Native UI library for C - with some extras
:radio_button: libui - Original version by andlabs.
Installation
It is recommended to use libui-ng, via the –pre commandline flag:
gem install libui --pre # libui-ng; this will fetch libui-0.1.3.pre-x86_64-linux.gem
If for some reason you would like to install the slightly older libui-0.1.2.gem release, issue:
gem install libui
-
The gem package includes the libui-ng shared library for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
-
Namely
libui.dll,libui.dylib, orlibui.so. -
No dependencies required.
-
The libui gem uses the standard Ruby library Fiddle to call C functions.
| Windows | Mac | Linux |
|---|---|---|
<img src=“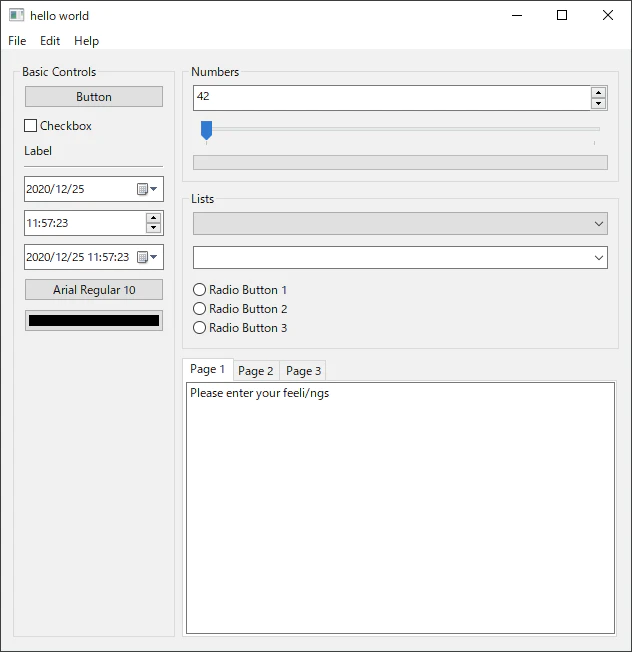 ”> ”> |
<img src=“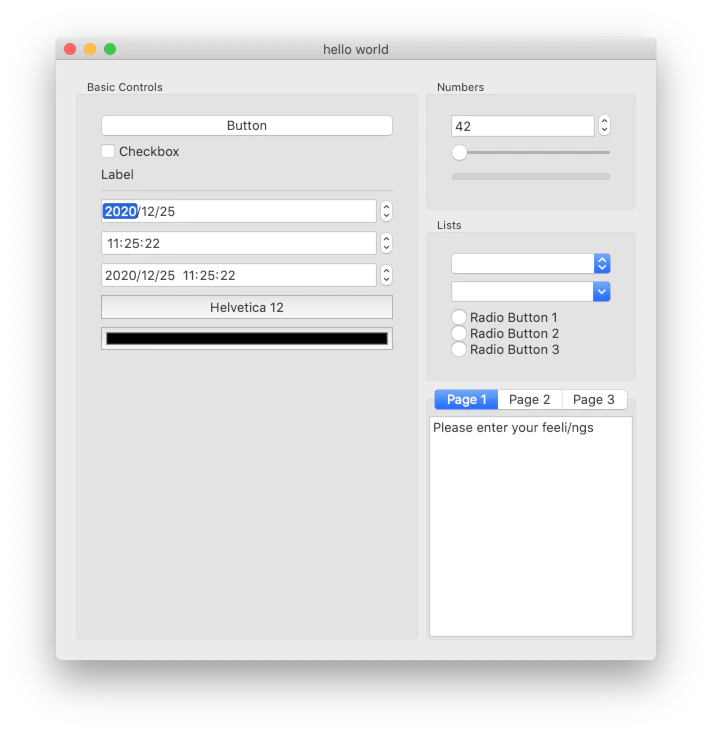 ”> ”> |
<img src=“ ”> ”> |
Notes:
-
If you are using the 32-bit (x86) version of Ruby, you need to download the 32-bit (x86) native dll. See the Development section.
-
On Windows, libui may not work due to missing DLLs. In that case, you need to install Visual C++ Redistributable. See (#48)
-
Users with Raspberry Pi or other platforms will need to compile the C libui library. See the Development section.
Usage
require 'libui'
UI = LibUI
UI.init
main_window = UI.new_window('hello world', 200, 100, 1)
= UI.('Button')
UI.() do
UI.msg_box(main_window, 'Information', 'You clicked the button')
end
UI.window_on_closing(main_window) do
puts 'Bye Bye'
UI.control_destroy(main_window)
UI.quit
0
end
UI.window_set_child(main_window, )
UI.control_show(main_window)
UI.main
UI.quit
For more examples, see the examples directory.
General Rules
Compared to the original libui library written in C:
-
Method names use snake_case.
-
The last argument can be omitted if it’s nil.
-
A block can be passed as a callback.
-
The block will be converted to a Proc object and added as the last argument.
-
The last argument can still be omitted when nil.
You can use the documentation for libui’s Go bindings as a reference.
DSLs for LibUI
LibUI is not object-oriented because it is a thin Ruby wrapper (binding) for the procedural C libui library, mirroring its API structure.
To build actual applications, it is recommended to use a DSL for LibUI, as they enable writing object-oriented code the Ruby way (instead of procedural code the C way):
Working with fiddle pointers
require 'libui'
UI = LibUI
UI.init
To convert a pointer to a string:
label = UI.new_label("Ruby")
p pointer = UI.label_text(label) # #<Fiddle::Pointer>
p pointer.to_s # Ruby
If you need to use C structs, you can do the following:
= UI.
# Allocate memory
font_descriptor = UI::FFI::FontDescriptor.malloc
font_descriptor.to_ptr.free = Fiddle::RUBY_FREE
# font_descriptor = UI::FFI::FontDescriptor.malloc(Fiddle::RUBY_FREE) # fiddle 1.0.1 or higher
UI.() do
UI.(, font_descriptor)
p family: font_descriptor.Family.to_s,
size: font_descriptor.Size,
weight: font_descriptor.Weight,
italic: font_descriptor.Italic,
stretch: font_descriptor.Stretch
end
-
Callbacks
-
In Ruby/Fiddle, a C callback function is written as an object of
Fiddle::Closure::BlockCallerorFiddle::Closure. Be careful about Ruby’s garbage collection - if the function object is collected, memory will be freed resulting in a segmentation violation when the callback is invoked.
# Assign to a local variable to prevent it from being collected by GC.
handler.MouseEvent = (c1 = Fiddle::Closure::BlockCaller.new(0, [0]) {})
handler.MouseCrossed = (c2 = Fiddle::Closure::BlockCaller.new(0, [0]) {})
handler.DragBroken = (c3 = Fiddle::Closure::BlockCaller.new(0, [0]) {})
Creating a Windows executable (.exe) with OCRA
OCRA (One-Click Ruby Application) builds Windows executables from Ruby source code.
To build an exe with Ocra, include 3 DLLs from the ruby_builtin_dlls folder:
ocra examples/control_gallery.rb ^
--dll ruby_builtin_dlls/libssp-0.dll ^
--dll ruby_builtin_dlls/libgmp-10.dll ^
--dll ruby_builtin_dlls/libffi-7.dll ^
--gem-all=fiddle ^
Add additional options below if necessary:
--window ^
--add-all-core ^
--chdir-first ^
--icon assets\app.ico ^
--verbose ^
--output out\gallery.exe
Development
git clone https://github.com/kojix2/libui
cd libui
bundle install
bundle exec rake vendor:auto # vendor:build
bundle exec rake test
Pre-built shared libraries for libui-ng
Use the following rake tasks to download the shared library required for your platform:
rake -T
rake vendor:build[hash] # Build libui-ng latest master [commit hash]
rake vendor:libui-ng:macos # Download latest official pre-build for Mac to vendor directory
rake vendor:libui-ng:ubuntu_x64 # Download latest official pre-build for Ubuntu to vendor directory
rake vendor:macos_arm64 # Download pre-build for Mac to vendor directory
rake vendor:macos_x64 # Download pre-build for Mac to vendor directory
rake vendor:raspbian_aarch64 # Download pre-build for Raspbian to vendor directory
rake vendor:ubuntu_x64 # Download pre-build for Ubuntu to vendor directory
rake vendor:windows_x64 # Download pre-build for Windows to vendor directory
rake vendor:windows_x86 # Download pre-build for Windows to vendor directory
For example, if you are using a 32-bit (x86) version of Ruby on Windows, type vendor:windows_x86. These shared libraries are artifacts of the pre-build branch of kojix2/libui-ng. In that case, please let us know.
Using C libui compiled from source code
The following Rake task will compile libui-ng. meson or ninja is required.
bundle exec rake vendor:build
Alternatively, you can tell Ruby LibUI the location of shared libraries. Set the environment variable LIBUIDIR to specify the path to the shared library. (See #46). This is especially useful on platforms where the LibUI gem does not provide shared library, such as the ARM architecture (used in devices like Raspberry Pi).
Another simple approach is to replace the shared libraries in the gem vendor directory with the ones you have compiled.
Publishing gems
ls vendor # check the vendor directory
rm -rf pkg # remove previously built gems
rake build_platform # build gems
# Check the contents of the gem
find pkg -name *.gem -exec sh -c "echo; echo \# {}; tar -O -f {} -x data.tar.gz | tar zt" \;
rake release_platform # publish gems
libui or libui-ng
-
From version 0.1.X, we plan to support only libui-ng/libui-ng.
-
Version 0.0.X only supports andlabs/libui.
Contributing
Would you like to contribute to LibUI?
-
Please feel free to send us your pull requests.
-
Small corrections, such as typo fixes, are appreciated.
-
Did you find any bugs? Submit them in the issues section!
Do you need commit rights?
-
If you need commit rights to my repository or want to get admin rights and take over the project, please feel free to contact @kojix2.
-
Many OSS projects become abandoned because only the founder has commit rights to the original repository.
Support libui-ng development
-
Contributing to the development of libui-ng is a contribution to the entire libui community, including Ruby’s LibUI.
-
For example, it would be easier to release LibUI in Ruby if libui-ng could be built easily and official shared libraries could be distributed.
Acknowledgements
This project is inspired by libui-ruby.
While libui-ruby uses Ruby-FFI, this gem uses Fiddle.